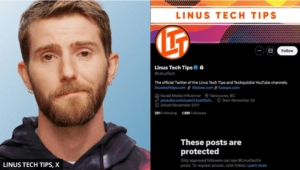
Last week, Linus Sebastian, the well-known tech personality behind Linus Tech Tips, faced a significant security breach when his official X (formerly Twitter) account was hacked. On August 12, 2024, the account was compromised and used to post fraudulent tweets promoting a fake sale of MacBook Pros for $600 each, claiming that all proceeds would go to charity and even offering free shipping and a signature from Linus himself. This highlights the importance of Recognizing Phishing emails
The hackers quickly took control of the account, changing the password and tampering with two-factor authentication (2FA), which effectively locked Linus out. Despite his attempts to regain access within minutes of receiving the alert, the hackers had already made changes that prevented him from doing so. He immediately warned his followers not to engage with the scam posts, criticizing X’s security protocols for not providing an immediate option to lock down the account in such situations.
A broader conversation has been sparked by the incident about the vulnerabilities that even high-profile accounts face on social media platforms and the need for more robust security features. As of now, the account has been set to private, and Linus and his team are working to regain full control.
Linus’s account of the event can be found on Friday’s WAN show episode.
Linus is a respected subject matter expert and definitely someone who ‘knows better’. This is a resounding wake-up call that if It can happen to him it can happen to any of us!
How to spot a password Phish…..
Among the various tactics employed by these criminals, phishing emails—particularly those disguised as password reset requests—are some of the most dangerous. These emails often look legitimate, tricking unsuspecting users into providing sensitive information. However, with the right knowledge, you can protect yourself and your business from falling victim to these scams. In this post, we’ll delve into the common characteristics of fraudulent password reset emails, how to recognize phishing emails, and what steps you should take if you suspect an email is fraudulent.
1. Understanding the Anatomy of a Phishing Email
Phishing emails are designed to look like they come from a trusted source, such as your bank, a popular online service, or even your own IT department. They often use urgent language to prompt immediate action, such as resetting a password. To identify a phishing email, it’s essential to understand the common elements that these fraudulent messages typically include:
- Sender Address: Phishing emails often come from addresses that look legitimate at first glance but contain subtle misspellings or extra characters. For example, an email might come from “support@go0gle.com” instead of “support@google.com.”
- Subject Line: The subject line of a phishing email is usually crafted to create a sense of urgency. It might say something like “Immediate Password Reset Required” or “Your Account Has Been Compromised.”
- Content: The body of the email often includes a link to a fake website where you’re prompted to enter your login credentials. The language used is usually generic and may contain spelling or grammatical errors, which are red flags.
- Branding: Phishers often use company logos and branding to make the email look authentic. However, these elements are often slightly off, either in color, size, or placement.
2. Recognizing a phishing email; The Red Flags
To protect yourself from phishing attacks and recognize phishing emails, it’s crucial to be vigilant and look out for specific red flags:
- Unusual Sender: Always check the sender’s email address carefully. If something looks off, it probably is. For example, if you receive an email from what appears to be PayPal but the sender’s address is something like “paypalsecurity123@gmail.com,” it’s a clear sign of a phishing attempt.
- Generic Greetings: Legitimate companies usually address you by your name, while phishing emails often use generic greetings like “Dear Customer” or “Dear User.”
- Unexpected Requests: Be suspicious of emails that ask you to reset your password, especially if you didn’t request a password reset. Reputable companies will never ask you to provide your password via email.
- Poor Grammar and Spelling: Many phishing emails originate from non-English-speaking countries and may contain noticeable spelling and grammar errors.
- Links and Attachments: Hover your mouse over any links in the email (without clicking) to see the URL. If the link doesn’t match the company’s official website or looks suspicious, don’t click it. Attachments in these emails may also contain malware.
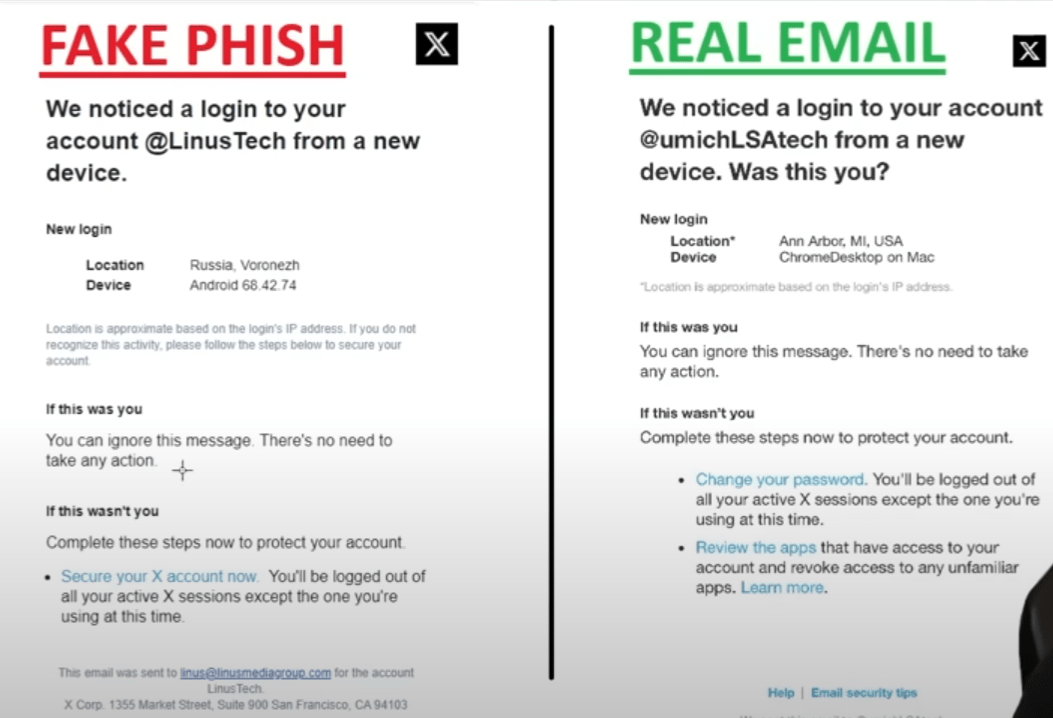
3. Examples of Phishing Emails
Understanding what the emails look like can help you recognize a phishing email. Here are a few examples of typical password reset phishing attempts:
Example 1: The Urgent Account Update
Subject: URGENT: Password Reset Required Immediately
Body:
“Dear Valued User,
Your account has been flagged for suspicious activity, and immediate action is required to secure your information. Please reset your password by clicking the link below.
Reset Your Password
Thank you for your prompt attention to this matter.
Sincerely, Security Team”
Example 2: The Fake Service Provider
Subject: [Service Name] Account Recovery
Body:
“Dear Customer,
We noticed unusual activity on your [Service Name] account and have temporarily locked it for your safety. To regain access, please click the link below and reset your password.
Reset Password Now
Regards, [Service Name] Support”
Example 3: The Spoofed Company Email
Subject: Important: Your Account Password Has Been Reset
Body:
“Dear User,
Your account password has been successfully reset. If you did not request this change, please click the link below to secure your account immediately.
Secure My Account
Best, [Company Name] Security Team”
Each of these examples demonstrates the tactics used by phishers to trick recipients into giving up their personal information. Notice the urgent tone, generic greetings, and suspicious links—all are classic signs of a phishing attempt.
4. How to Handle Suspicious Emails
If you receive an email that you suspect is a phishing attempt, follow these steps to protect yourself:
- Do Not Click Links or Download Attachments: Clicking on a link or downloading an attachment from a phishing email can lead to malware installation or redirect you to a fraudulent website designed to steal your information.
- Verify the Sender: If the email appears to be from a legitimate company, contact them directly using a phone number or website you know is authentic. Don’t use the contact information provided in the suspicious email.
- Report the Phishing Attempt: Many companies, including Google, Microsoft, and PayPal, have dedicated email addresses where you can forward phishing attempts. Reporting these emails helps prevent others from falling victim.
- Delete the Email: Once you’ve reported the phishing attempt, delete the email from your inbox and your trash or deleted items folder to prevent any accidental clicks in the future.
5. Best Practices for Staying Safe
While it’s important to recognize phishing emails, it’s equally crucial to follow best practices to protect yourself proactively:
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): 2FA adds an extra layer of security by requiring you to provide a second form of identification, such as a code sent to your phone, in addition to your password.
- Use Strong, Unique Passwords: Avoid using the same password for multiple accounts. Strong passwords should include a mix of letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Regularly Update Passwords: Change your passwords regularly to reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
- Educate Your Team: Ensure that everyone in your organization is aware of phishing tactics and knows how to identify suspicious emails.
- Keep Software Updated: Regularly update your operating system, browsers, and antivirus software to protect against the latest threats.
- Install Reliable Endpoint Protection: Many modern endpoint protection software packages are capable of recognizing phishing email links.
6. What to Do If You Fall Victim
Despite your best efforts, it’s still possible to fall for a phishing scam. If you realize you’ve provided your information to a fraudulent site, take the following steps immediately:
- Change Your Password: If you’ve entered your password on a fake site, change it immediately on the legitimate site. Also, update any other accounts that use the same password.
- Monitor Your Accounts: Keep a close eye on your bank accounts, credit cards, and other online accounts for any unauthorized transactions.
- Contact Your Bank: If you suspect that your financial information has been compromised, secure your accounts by contacting your bank or credit card company.
- Run a Security Scan: Detect and remove any malware that may have been installed by using antivirus software to run a full system scan.
- Report the Incident: Report the phishing attack to your email provider, the company that was impersonated, and, if necessary, law enforcement.
Conclusion
Phishing emails, particularly those disguised as password reset requests, are a common tool used by cybercriminals to steal sensitive information. By understanding the common traits of these emails and following the steps outlined in this post, you can protect yourself and your business from falling victim to these scams. Always stay vigilant, educate your team, and take proactive measures to enhance your cybersecurity. Remember, when it comes to online security, a little caution goes a long way.


